What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Unlike traditional diets, IF does not focus on specific foods to eat but rather on when you should eat them.
Methods of Intermittent Fasting
There are several popular methods of intermittent fasting:
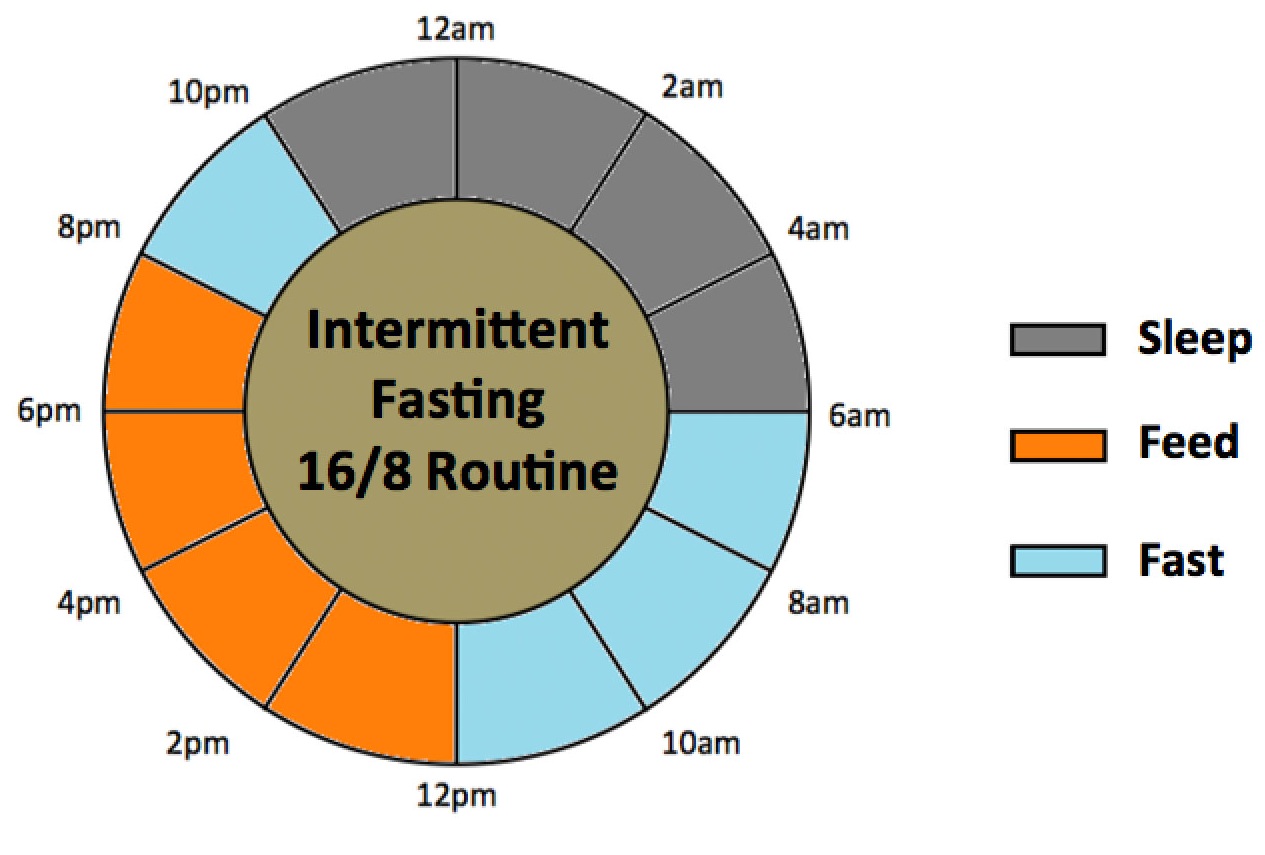
- 16/8 Method: Involves fasting for 16 hours each day and eating during an 8-hour window. Commonly, people skip breakfast and eat from noon to 8 p.m.
- 5:2 Diet: Involves eating normally for 5 days of the week and consuming only about 500-600 calories on the other 2 days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: Involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week. For example, not eating from dinner one day until dinner the next day.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Involves alternating between days of normal eating and days of fasting or eating very little.
- Warrior Diet: Involves eating small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and having one large meal at night, typically within a 4-hour window.

Effects of Intermittent Fasting
- Cellular Repair: Fasting initiates autophagy, a process where cells remove damaged components.
- Hormonal Changes: Insulin levels drop, and growth hormone levels increase, facilitating fat burning and muscle gain.
- Gene Expression: Fasting triggers beneficial changes in genes related to longevity and protection against diseases.
Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting can help with weight loss by reducing the overall calorie intake and increasing metabolic rate. By eating fewer meals, you might naturally consume fewer calories. Additionally, fasting enhances hormone function to facilitate weight loss.
Benefits
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Can lower blood sugar levels and protect against type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Health: May reduce risk factors such as cholesterol levels, inflammatory markers, blood sugar, and insulin resistance.
- Brain Health: Enhances brain function and can increase the growth of new neurons. Also may protect against Alzheimer’s disease.
- Longevity: Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting can extend lifespan.
Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting
- Individuals with a history of eating disorders.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Those with certain medical conditions, like diabetes, without doctor supervision.
- People who are underweight or have nutrient deficiencies.
Safety
Intermittent fasting is generally safe for healthy individuals, but it’s crucial to listen to your body and ensure you are getting enough nutrients during eating periods. If you experience adverse effects or have pre-existing health conditions, consult a healthcare professional before starting.
FAQs
- Can I drink liquids during the fasting period?
Yes, water, coffee, tea, and other non-caloric beverages are allowed. Avoid adding sugar, but small amounts of milk or cream may be okay.
- Will fasting cause muscle loss?
All weight loss methods can cause some muscle loss, but intermittent fasting and weight training can help mitigate this effect.
- Can I exercise while fasting?
Yes, but it’s important to pay attention to how you feel. Some people may prefer to schedule workouts during their eating windows.
- How long should I fast?
It depends on the method you choose. Common practices range from 14-24 hours of fasting.
- Will fasting slow down my metabolism?
Short-term fasting actually increases metabolism. Long-term fasting or severe calorie restriction can reduce metabolic rate.
Intermittent fasting can be an effective and flexible approach to improving health and managing weight, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Always consider personal health conditions and consult with a healthcare provider if unsure.